
Pictures of Endosporobacteria:







Characteristics of Endosporobacteria:
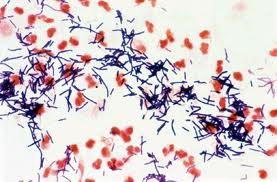
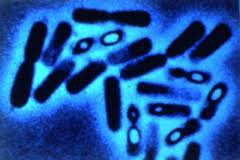
The Endosporobacteria receive this name because some of their representatives are capable of forming intracellular spores (endo means interior). They are ubiquitous organisms, generally aerobic, that can become fermentative anaerobes, and can live freely in soil and water, be parasites or symbionts. They are heterotrophs (consuming foreign organic matter) with some exceptions capable of photosynthesis (like Heliobacterium). Many of these species are necessary for digestion in herbivorous organisms (such as termites), so they reside in specialized structures in the intestines of these animals. They are abundant organisms in the human intestine, playing an important role in digestive processes and nutrient absorption. Additionally, many species live as commensals on animal skins, including humans, although they can become potent pathogens if they acquire the necessary genes to attack the host. Some fermentative species are used to produce yogurts, cheeses, and other lactic ferments.
Phylum: Endosporobacteria